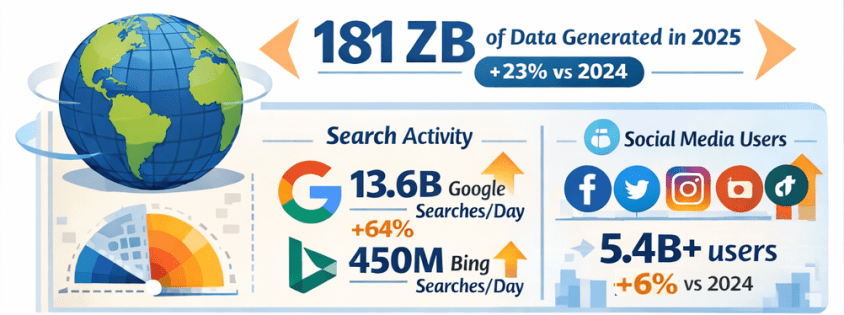
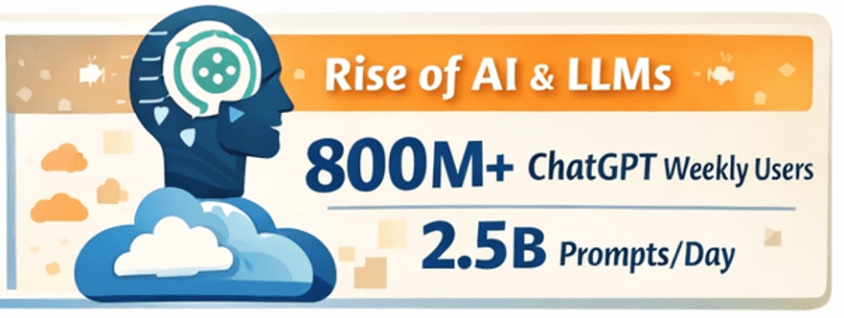
Marketing has always been about understanding people—what they want, when they want it, and how best to reach them. What’s changed is the scale and complexity of that challenge. Customers interact across dozens of channels, generate massive amounts of data, and expect personalization as the default.
AI has become the connective tissue that allows marketing teams to turn fragmented data into insight, automation, and growth—often in real time.
How AI Is Being Used in Marketing Today
AI now touches nearly every part of the marketing function:
Personalization & Customer Segmentation
- Netflix uses AI to personalize thumbnails, recommendations, and messaging—driving engagement and retention.
- Amazon applies machine learning to personalize product recommendations and promotions across its marketing channels.
Content Creation & Optimization
- Coca-Cola has used generative AI tools to co-create marketing content and creative assets.
- Marketing teams use OpenAI models (via ChatGPT and APIs), Adobe Firefly, and Jasper AI to generate copy, images, and ad variations at scale.
Marketing Automation & Campaign Optimization
- Salesforce Einstein optimizes email send times, predicts customer engagement, and recommends next-best actions.
- HubSpot AI assists with content generation, lead scoring, and campaign optimization.
Paid Media & Ad Targeting
- Meta Advantage+ and Google Performance Max use AI to automate bidding, targeting, and creative optimization across ad networks.
Customer Journey Analytics
- Adobe Sensei analyzes cross-channel customer journeys to identify drop-off points and optimization opportunities.
Voice, Chat, and Conversational Marketing
- Brands use AI chatbots and virtual assistants for lead capture, product discovery, and customer support.
Tools, Technologies, and Forms of AI in Use
Modern marketing AI stacks typically include:
- Machine Learning & Predictive Analytics
Used for churn prediction, propensity scoring, and lifetime value modeling. - Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Powers content generation, sentiment analysis, and conversational interfaces. - Generative AI & Large Language Models (LLMs)
Used to generate ad copy, emails, landing pages, social posts, and campaign ideas.- Examples: ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, Jasper, Copy.ai
- Computer Vision
Applied to image recognition, brand safety, and visual content optimization. - Marketing AI Platforms
- Salesforce Einstein
- Adobe Sensei
- HubSpot AI
- Marketo Engage
- Google Marketing Platform
Benefits Marketers Are Realizing
Organizations that adopt AI effectively see significant advantages:
- Higher Conversion Rates through personalization
- Faster Campaign Execution with automated content creation
- Lower Cost per Acquisition (CPA) via optimized targeting
- Improved Customer Insights and segmentation
- Better ROI Measurement and attribution
- Scalability without proportional increases in headcount
In many cases, AI allows small teams to operate at enterprise scale.
Pitfalls and Challenges
Despite its power, AI in marketing has real risks:
Over-Automation and Brand Dilution
- Excessive reliance on generative AI can lead to generic or off-brand content.
Data Privacy and Consent Issues
- AI-driven personalization must comply with GDPR, CCPA, and evolving privacy laws.
Bias in Targeting and Messaging
- AI models can unintentionally reinforce stereotypes or exclude certain audiences.
Measurement Complexity
- AI-driven multi-touch journeys can make attribution harder, not easier.
Tool Sprawl
- Marketers may adopt too many AI tools without clear integration or strategy.
Where AI Is Headed in Marketing
The next wave of AI in marketing will be even more integrated and autonomous:
- Hyper-Personalization in Real Time
Content, offers, and experiences adapted instantly based on context and behavior. - Generative AI as a Creative Partner
AI co-creating—not replacing—human creativity. - Predictive and Prescriptive Marketing
AI recommending not just what will happen, but what to do next. - AI-Driven Brand Guardianship
Models trained on brand voice, compliance, and tone to ensure consistency. - End-to-End Journey Orchestration
AI managing entire customer journeys across channels automatically.
How Marketing Teams Can Gain an Advantage
To thrive in this fast-changing environment, marketing organizations should:
- Anchor AI to Clear Business Outcomes
Start with revenue, retention, or efficiency goals—not tools. - Invest in Clean, Unified Customer Data
AI effectiveness depends on strong data foundations. - Establish Human-in-the-Loop Workflows
Maintain creative oversight and brand governance. - Upskill Marketers in AI Literacy
The best results come from marketers who know how to prompt, test, and refine AI outputs. - Balance Personalization with Privacy
Trust is a long-term competitive advantage. - Rationalize the AI Stack
Fewer, well-integrated tools outperform disconnected point solutions.
Final Thoughts
AI is transforming marketing from a campaign-driven function into an intelligent growth engine. The organizations that win won’t be those that simply automate more—they’ll be the ones that use AI to understand customers more deeply, move faster with confidence, and blend human creativity with machine intelligence.
In marketing, AI isn’t replacing storytellers—it’s giving them superpowers.