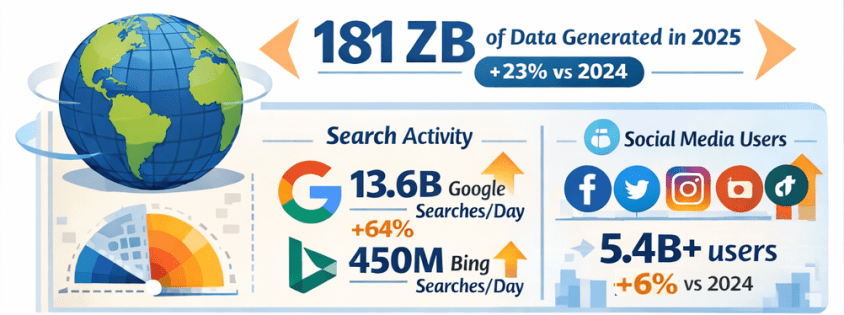
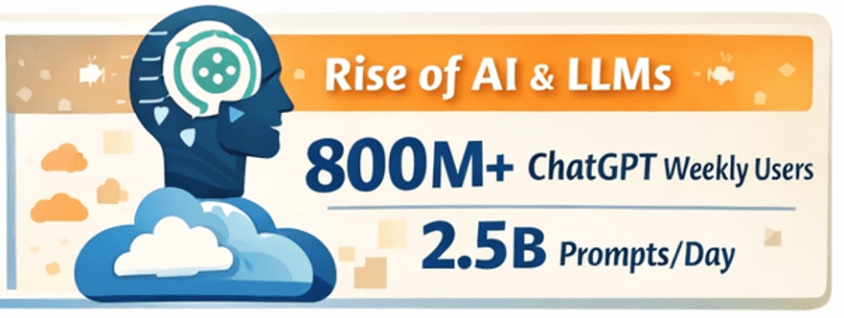
Agriculture has always been a data-driven business—weather patterns, soil conditions, crop cycles, and market prices have guided decisions for centuries. What’s changed is scale and speed. With sensors, satellites, drones, and connected machinery generating massive volumes of data, AI has become the engine that turns modern farming into a precision, predictive, and increasingly autonomous operation.
From global agribusinesses to small specialty farms, AI is reshaping how food is grown, harvested, and distributed.
How AI Is Being Used in Agriculture Today
Precision Farming & Crop Optimization
- John Deere uses AI and computer vision in its See & Spray™ technology to identify weeds and apply herbicide only where needed, reducing chemical use by up to 90% in some cases.
- Corteva Agriscience applies AI models to optimize seed selection and planting strategies based on soil and climate data.
Crop Health Monitoring
- Climate FieldView (by Bayer) uses machine learning to analyze satellite imagery, yield data, and field conditions to identify crop stress early.
- AI-powered drones monitor crop health, detect disease, and identify nutrient deficiencies.
Autonomous and Smart Equipment
- John Deere Autonomous Tractor uses AI, GPS, and computer vision to operate with minimal human intervention.
- CNH Industrial (Case IH, New Holland) integrates AI into precision guidance and automated harvesting systems.
Yield Prediction & Forecasting
- IBM Watson Decision Platform for Agriculture uses AI and weather analytics to forecast yields and optimize field operations.
- Agribusinesses use AI to predict harvest volumes and plan logistics more accurately.
Livestock Monitoring
- Zoetis and Cainthus use computer vision and AI to monitor animal health, detect lameness, track feeding behavior, and identify illness earlier.
- AI-powered sensors help optimize breeding and nutrition.
Supply Chain & Commodity Forecasting
- AI models predict crop yields and market prices, helping traders, cooperatives, and food companies manage risk and plan procurement.
Tools, Technologies, and Forms of AI in Use
Agriculture AI blends physical-world sensing with advanced analytics:
- Machine Learning & Deep Learning
Used for yield prediction, disease detection, and optimization models. - Computer Vision
Enables weed detection, crop inspection, fruit grading, and livestock monitoring. - Remote Sensing & Satellite Analytics
AI analyzes satellite imagery to assess soil moisture, crop growth, and drought conditions. - IoT & Sensor Data
Soil sensors, weather stations, and machinery telemetry feed AI models in near real time. - Edge AI
AI models run directly on tractors, drones, and field devices where connectivity is limited. - AI Platforms for Agriculture
- Climate FieldView (Bayer)
- IBM Watson for Agriculture
- Microsoft Azure FarmBeats
- Trimble Ag Software
Benefits Agriculture Companies Are Realizing
Organizations adopting AI in agriculture are seeing tangible gains:
- Higher Yields with fewer inputs
- Reduced Chemical and Water Usage
- Lower Operating Costs through automation
- Improved Crop Quality and Consistency
- Early Detection of Disease and Pests
- Better Risk Management for weather and market volatility
In an industry with thin margins and increasing climate pressure, these improvements are often the difference between profit and loss.
Pitfalls and Challenges
Despite its promise, AI adoption in agriculture faces real constraints:
Data Gaps and Variability
- Farms differ widely in size, crops, and technology maturity, making standardization difficult.
Connectivity Limitations
- Rural areas often lack reliable broadband, limiting cloud-based AI solutions.
High Upfront Costs
- Autonomous equipment, sensors, and drones require capital investment that smaller farms may struggle to afford.
Model Generalization Issues
- AI models trained in one region may not perform well in different climates or soil conditions.
Trust and Adoption Barriers
- Farmers may be skeptical of “black-box” recommendations without clear explanations.
Where AI Is Headed in Agriculture
The future of AI in agriculture points toward greater autonomy and resilience:
- Fully Autonomous Farming Systems
End-to-end automation of planting, spraying, harvesting, and monitoring. - AI-Driven Climate Adaptation
Models that help farmers adapt crop strategies to changing climate conditions. - Generative AI for Agronomy Advice
AI copilots providing real-time recommendations to farmers in plain language. - Hyper-Localized Decision Models
Field-level, plant-level optimization rather than farm-level averages. - AI-Enabled Sustainability & ESG Reporting
Automated tracking of emissions, water use, and soil health.
How Agriculture Companies Can Gain an Advantage
To stay competitive in a rapidly evolving environment, agriculture organizations should:
- Start with High-ROI Use Cases
Precision spraying, yield forecasting, and crop monitoring often deliver fast payback. - Invest in Data Foundations
Clean, consistent field data is more valuable than advanced algorithms alone. - Adopt Hybrid Cloud + Edge Strategies
Balance real-time field intelligence with centralized analytics. - Focus on Explainability and Trust
Farmers need clear, actionable insights—not just predictions. - Partner Across the Ecosystem
Collaborate with equipment manufacturers, agritech startups, and AI providers. - Plan for Climate Resilience
Use AI to support long-term sustainability, not just short-term yield gains.
Final Thoughts
AI is transforming agriculture from an experience-driven practice into a precision, intelligence-led system. As global food demand rises and environmental pressures intensify, AI will play a central role in producing more food with fewer resources.
In agriculture, AI isn’t replacing farmers—it’s giving them better tools to feed the world.